Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun: 베트남 미기록종
Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun (Capparaceae): A newly recorded species of the flora of Vietnam
Article information
Abstract
Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun를 베트남의 미기록종으로 보고한다. 본 종은 형태적으로 C. sikkimensis Kurz와 유사하지만, 소지 위의 털이 회색빛을 띄는 황색이며, 이차맥의 수가 더 많고, 꽃잎 양면 모두에 선모가 있으며, 열매가 구형인 점에서 차이가 난다. 본 종은 현재까지 중국의 광서성과 운남성에서만 보고되었다. 본 종의 동정을 위해 기재, 도해 및 컬러사진을 제공하였다. 더불어, 관련종과의 형태형질에 대한 비교자료를 제시하였다.
Trans Abstract
Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun is reported here as a new addition to the flora of Vietnam. It is morphologically allied to C. sikkimensis Kurz but differs due to the gray-yellow color of the hair of the twigs, having more secondary veins on the leaf, trichomes on both surfaces of the petal, and a globose shape of the fruit. Thus far, it has only been reported in the Guangxi and Yunnan areas of China. A description, a line drawing and color photographs are provided for species identification. Furthermore, a comparison of the diagnostic characters with those of related species is made.
The genus Capparis L. is represented by between 250–400 species in the world (Zhang and Tucker, 2008). Capparis species have been known as a good food resource because its floral buds and fruits contain minerals, protein, carbohydrates, lipids and vitamins (Prashant et al., 2016). However, it is difficult taxon to identify taxonomically because their vegitative characters are similar and confued without sexual characters. Up to now, 36 species, 3 subspecies, and 2 varieties are reported including one new species which discovered recently in Vietnam (Thuong et al., 2013, 2015, 2016). An additional new record species was found during regular field trip between Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources (IEBR) and Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) to Loc Binh District, Lang Son Province in 2015 (Fig. 1). Morphological characters of this plant were matched with another unidentified specimen which was housed in the herbarium of Institute of Medicinal Materies (HNPM) and the herbarium of Vietnam Forest Museum (VFM) of Forest Inventory and Planning Institute. Finally, we identified them as a C. pubifolia through careful checking a type specimen and literature survey (Jacobs, 1965; How, 1979; Pham, 1999; Wu, 1999; Zhang and Tucker, 2008). It is morphologically allied to C. sikkimensis Kurz but differs by gray-yellow color of hair on twigs, having more number of secondary vein on leaf, trichomes on both surfaces of petal and globose shape of fruit (Table 1). This taxon was found only from Guangxi and Yunnan areas of China (Zhang and Tucker, 2008) but never recordedin Vietnam. A detailed description along with line drawing and photographs (Figs. 2, 3) has been provided to support species identification.

Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun. A. Flowering twig. B. Part of stem. C. Stem with spines. D. Lower surface of leaf. E. Flora bud. F. Outer sepal. G. Pistil with gynophore and ovary. H. Ovary. I. Fruit (illustration drawn by Le Kim Chi). Based on specimens B. X. Thuan 452 (VFM) (A–H), Trai, Son, Long, Tuan 7804D (HNPM) (I).
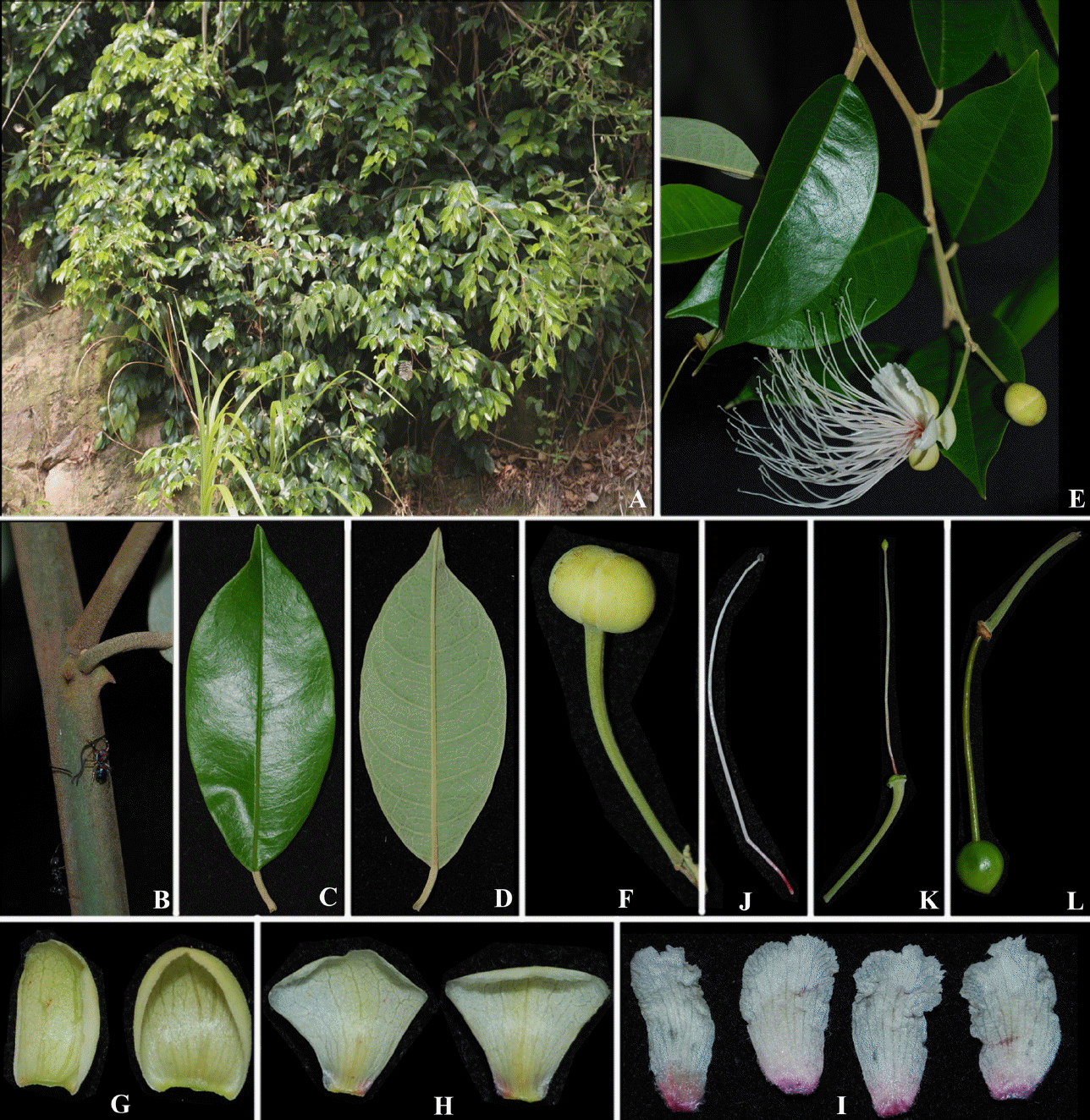
Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun. A. Habit. E. Flowering twig. B. Stem with spines. C. Upper surface of leaf. D. Lower surface of leaf. F. Floral bud. J. Stamen. K. Pistil with gynophore and ovary. L. Young fruit. G. Outer sepal pairs. H. Inner sepal pairs. I. Petals (photographs by Tran The Bach and Do Van Hai).
Taxonomic Treatment
Capparis pubifolia B. S. Sun in C. Y. Wu, Fl. Yunnan 2: 64, 1979 (Figs. 1, 2).—TYPE: CHINA. Zhang Zhao Qian 13028 (holotype: IBSC-Photo!).
Scandent shrubs up to 5 m tall. Twigs densely gray-yellow tomentose. Spines 0.5–1 mm long, recurved downwards, apex sharp, with gray-yellow tomentose. Petiole 0.8–1 cm long, hairy like those on twigs. Leaves simple, alternate; leaf blade ovate or elliptic, 4.5–8 × 2.5–3.5 cm, abaxially densely gray-yellow persistently tomentose, adaxially tomentose only on midvein; secondary veins 9–12, connected near the margin, abaxially raised and hairy as on twigs, adaxially slightly raised; base round or cuneate; apex acuminate, 0.5–0.7 cm long. Inflorescences corymbs, axillary or terminal, 5–5.5 cm long; peduncle and pedicel tomentose like those on twigs, peduncle 2–3 cm long, pedicels 1.5–2 cm long. Floral buds globose, 0.5– 0.6 cm in diam. Sepals 4; outer sepals whorl boat-shape, pale green, 4–6 × 8–9 mm, tomentose outside, glabrous inside; inner sepals whorl obovate, pale white but pink at the corner of the base, 10–11 × 9–9.5 mm, trichomes only at the base. Petals 4, almost white and pink at the base, obovate, trichomes on both surfaces, especially at the base. Stamens 43–50; filaments 2.5– 3 cm long, base red; anthers ca. 1 mm long, white-gray. Gynophore 4–4.2 cm long, glabrous. Ovary oval, 2 ×1 mm, apex acute, glabrous. Fruit baccate, nearly globose, 2– 2.1 × 1.7–1.8 cm, smooth, apex beaked when young.
Flowering: July.
Fruiting: July–September
Ecology and habitat: Capparis pubifolia was found growing on a rocky slope, at elevation about 415–500 m in association with Chromolaena odorata (L.) R. M. King & H. Rob., Saccharum spontaneum L., Gleichenia linearis (Burm. f.) C. B. Clarke, Trema orientalis (L.) Blume and Mallotus barbatus Müll.-Arg.
Distribution: China (Guangxi, Yunnan) and Vietnam (Bac Kan, Lang Son Province).
Specimens examined: VIETNAM. Bac Kan Province: Bach Thong District, Sy Binh commune, 26 Aug 2004, Trai, Son, Long, Tuan 7804A, 7804B, 7804C, 7804D, 7804E, 7804F (HNPM). Lang Son Province: Cao Loc District, Cong Son commune, 3 Jul 1969, Thuan BX 452, BX 453 (VFM). Lang Son Province: Loc Binh District, Bang Khanh commune, 20 Jul 2015, 21°48′41.4″N, 106°52′39.9″E, 415 m, Bach, Binh, Chinh, Hai, Quang, SonVK 6501 (HN).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the collaborative project between Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources (IEBR) and International Biological Material Research Center (IBMRC), Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology and funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 106-NN.03-2015.20 and The National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NRF-2016K1A1A8A 01939075). We also thank to the curators of herbarium of Institute of Medicinal Materials (HNPM), herbarium of Vietnam Forest Museum (VFM) – Forest Inventory, Planning Institute and the botanists of Institute of Ecology and Biological Resources – Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi for permitting us to study the voucher specimens.